This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 642224
This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 642224
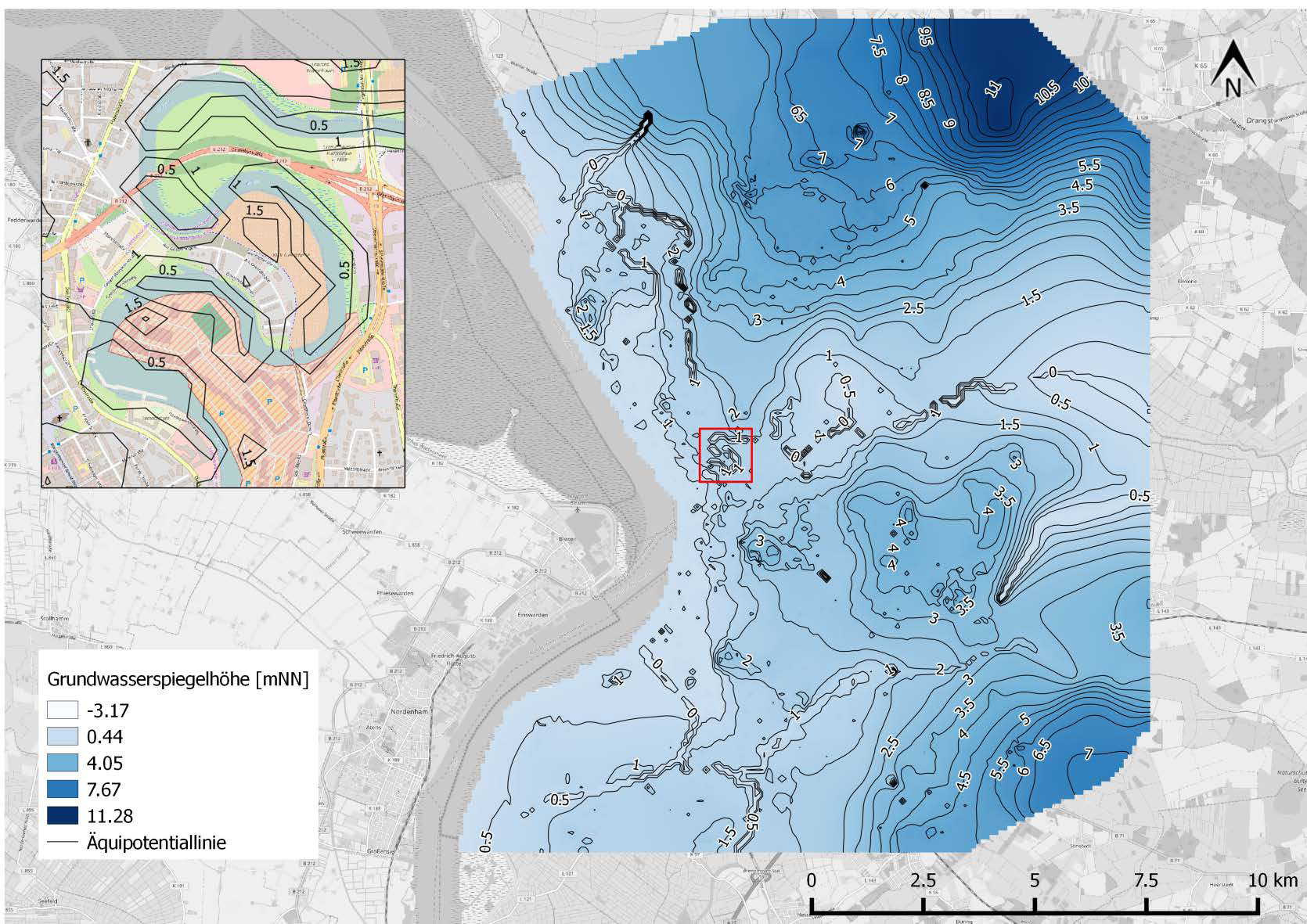
With the Bremerhaven case study, a tool is provided to manage a coastal quaternary aquifer. Bremerhaven is a city in the northern part of Germany east to the river Weser estuary nearby the North Sea. The city covers about 93.82 km2 and has a population of 114000. Two waterworks located in the north and the south of the city supply the inhabitants with drinking water. Additional there are some other withdrawals in the area for other purposes. Due to its geographical position the aquifer is affected by tidal influence and saltwater intrusion. In some areas the aquifer is also affected by linked surface water bodies. We are dealing with a sandy aquifer which is partly covered by confining sediments. In some areas the aquifer is free.
An aim of the FREEWAT case study is to predict the impact of sea level rise and changing amounts of recharge due to climate change to the aquifer. The tool should help to fully understand the aquifer system and ensure a secure water supply for the next decades.